Link State Routing Step By Step
Link State Routing Step By Step Distance vector routing was utilized in the ARPANET till 1979, once it had been replaced by link state routing. Two primary problems caused its demise. First, since the delay metric was queue length, it failed to take line information measure into consideration once selecting routes. Initially, all the lines were 56 kbps, so line bandwidth was not an issue, but after some lines had been upgraded to 230 kbps and others ta 1544 Mbps, not taking bandwidi into account was a major prodlem. Of course, it might are potential to alter the delay metric to consider line information measure, however a second downside conjointly existed, namely, the algorithm often took too long to converge, even with tricks like split horizon. For these reasons, it was replaced by an entirely new algorithm now called link state routing. Vari ants of link state routing square measure currently wide used. The idea behind link state routing is easy and may be declared as 5 components.
Each router must
- Discover its neighbors and leam their network addresses
- Measure the delay or cost to each of its neighbors.
- Construct a packet telling all it has just learned.
- Send this packet to all other routers.
- Compute the shortest path to every other router.
In result the whole topology and every one delays area unit through an experiment measured and distributed to each router. Then Dijkstra’s algorithmic rule is wont to realize the shortest path to each different router. Below we will consider each of these five steps in more detail.
Learning about the Neighbors
When a router is shodden, its 1st task is to find out WHO its neighbors ar. It accomplishes this goal by causation a special how-do-you-do packet on every point-to-point line. The router on the opposite finish is anticipated to remand a reply telling WHO it’s. These names should be globally distinctive as a result of once a far off router later hears that 3 routers ar all connected to F, it’s essential that it will verify whether or not or not all three mean the same F. When 2 or a lot of routers ar connected by a computer network, the case is slightly a lot of sophisticated. Fig. 5-13(a) illustrates a LAN to which three routers, A, C, ind F, are directly connected. Each of those routers is connected to 1 or a lot of extra routers, as shown.
One way to model the LAN is to consider it as a node itself, as shown in Fig. 5-13(b). Here we’ve introduced a replacement, artificial node, N, to which A, C, and F are connected. The fact that it’s potential to travel from A to C on the computer network is delineated by the trail ANC here.
Measuring Line Cost
The connection state steering calculation requires every switch to know, or possibly have a sensible gauge of the deferral to every one of its neighbors. The most immediate approach to decide this postponement is to send a unique ECHO parcel over the line that the opposite side is required to send back right away. By estimating the full circle time and isolating it by two, the sending switch can get a sensible gauge of the deferral. For far better outcomes, the test can be directed a few times, and the normal utilized. A fascinating issue is whether to consider the heap when estimating the deferral. To figure the heap, the full circle clock must be begun when the ECHO parcel is lined. To disregard the heap, the clock ought to be begun when the ECHO parcel arrives at the front of the line. Contentions can be made the two different ways. Counting traffic-incited delays in the estimations implies that when a switch has a decision between two lines with a similar data transfer capacity, one of which is intensely stacked constantly and one of which isn’t, it will respect the course over the emptied line as a shorter way.
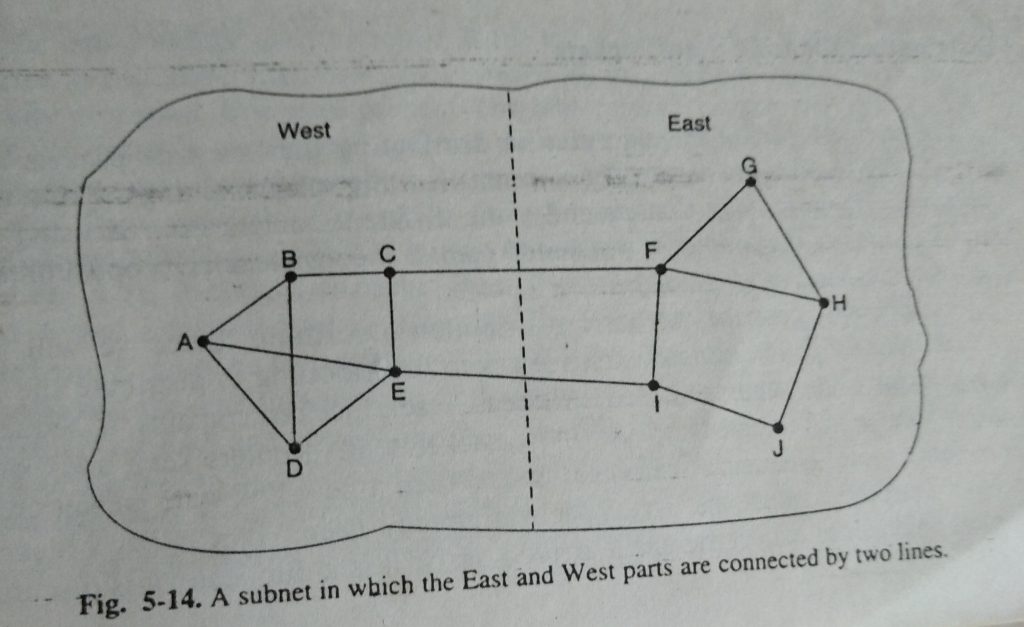
This decision will bring about better execution. Shockingly, there is additionally a contention against remembering the heap for the postpone figuring. Consider the subnet of Fig. 5-14, which is split into two sections, East and West, associated by two lines, CF and EI. Assume that mos me traffic among East and West is utilizing line CF, and therefore, is intensely stacked with long postponements. Counting queueing delay in the most limited way figuring will make U increasingly appealing. After the new directing tables have been introduced, the majority of the East-West traffic will currently go over El, over-burdening this line. Therefore, in the following update, CF will give off an impression of being the most brief way. Subsequently, the steering tables may waver uncontrollably, prompting sporadic directing and numerous potential issues. On the off chance that heap is overlooked and just data transfer capacity is considered, this issue doesn’t happen. On the other hand, the heap can be spread over the two lines, yet this arrangement doesn’t completely use the best way.
Building Link State Packets
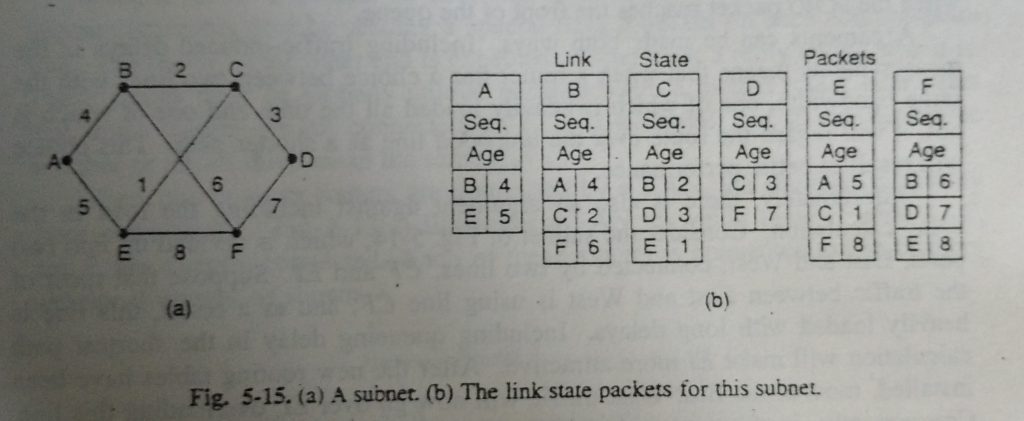
When the data required for the trade has been gathered, the following stage is for every switch to construct a bundle containing every one of the information. The parcel begins with the character of the sender, trailed by a succession number and age (to be depicted later), and a rundown of neighbors. For each neighbor, the postponement to that neighbor is given. A model subnet is given in Fig. 5-15(a) with delays appeared in the lines. The relating join state parcels for every one of the six switches are appeared.
Building the connection state parcels is simple. The critical step is deciding when to assemble them. One probability is to assemble them intermittently, that is, at customary interims. Another probability is the point at which some critical occasion happens, for example, a line or neighbor going down or returning up once more, or changing its properties considerably.
For know more
HOME PollyBD Networking Blogspot
PollyBD Networking Blogspot